In recent years, the European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of implementing regulations to protect consumer rights and promote sustainability. One such regulation that has garnered attention is the EU’s rule on user-replaceable batteries for electronic devices, including smartphones. This rule aims to empower consumers by ensuring they can easily remove and replace the batteries in their devices. However, there have been concerns regarding the impact of this rule on the IP (Ingress Protection) rating of mobile phones, particularly regarding water resistance. This article will examine the correlation between the law concerning user-replaceable batteries in the European Union (EU) and the IP rating found on mobile devices.

Understanding the EU User Replaceable Batteries Rule
The EU user-replaceable batteries rule requires manufacturers to design electronic devices, including smartphones, so consumers can easily remove and replace them. Machines should not be sealed off to prevent battery access, and specialized tools or knowledge should not be required for battery replacement.
The rule is part of a broader effort to create a circular economy and reduce electronic waste. By enabling users to replace batteries, it becomes easier to extend the lifespan of devices, reducing the need for frequent upgrades and ultimately reducing the environmental impact.
Mobile phones have evolved into an indispensable aspect of our everyday routines, making the durability and functionality of these devices pivotal for consumers. The EU’s user-replaceable batteries rule promotes sustainability by reducing electronic waste and giving consumers greater control over their devices. However, questions have arisen regarding the compatibility of this rule with the IP rating, which denotes a device’s resistance to water and dust.
The Importance of IP Rating on Mobiles
IP ratings are a standard system used to measure and communicate the degree of protection a device provides against solids (dust) and liquids (water). The IP rating is usually followed by two digits, where the first digit represents the device’s dust resistance and the second digit represents its water resistance.
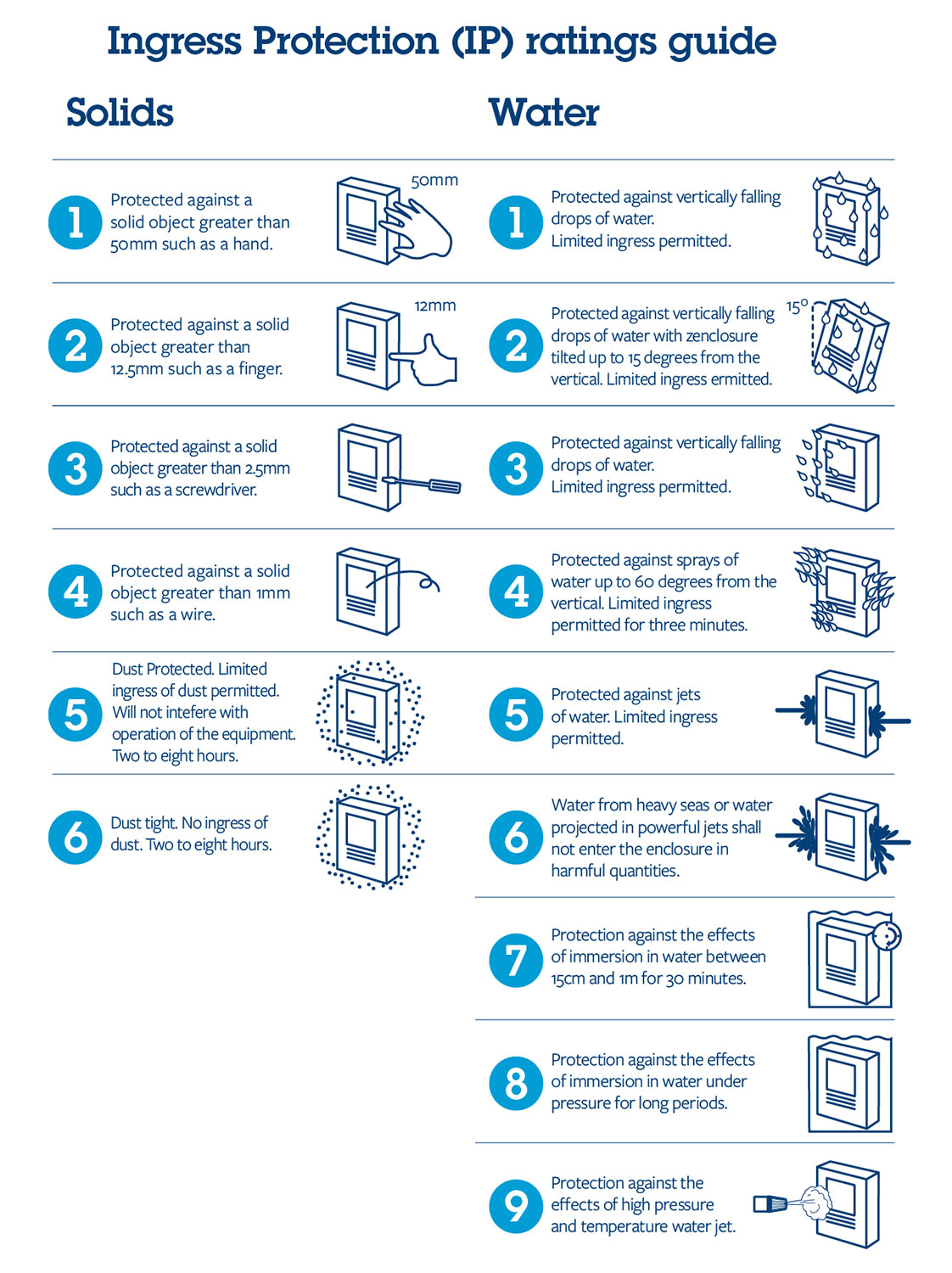
For example, an IP68 rating is commonly found in high-end smartphones, indicating that the device is dust-tight and can withstand immersion in water up to a certain depth for a specified duration. IP68 is currently the highest rating for consumer mobile devices, providing increased protection against dust and moisture.
Challenges in Achieving Both EU Battery Replaceability and IP Rating Water and Dust Resistance
The challenge arises when combining user-replaceable batteries with high IP ratings. Ensuring water resistance requires effectively sealing a device’s internal components, preventing water from entering sensitive areas. On the other hand, facilitating battery replaceability involves creating access points to remove and replace the battery.
Phones already have openings for speakers and charger ports, yet they can still maintain their water resistance. This is because the design allows for effective sealing of these openings, ensuring water does not infiltrate the internal components. However, the situation becomes more complex when it comes to battery doors.
A battery door needs to create a secure seal to prevent water from entering the device, which becomes challenging when considering the frequency of open and close events and exposure to dirt and debris. Maintaining a thin device profile while accommodating these requirements adds further complexity to the design process.
Potential Solutions and Technological Advancements
Manufacturers and researchers have been exploring various solutions to address the challenge of combining battery replaceability with high IP ratings. One potential solution involves developing innovative sealing techniques and materials that can provide robust protection against water while allowing easy battery access.
Advancements in nano-coatings and adhesives have shown promise in creating effective seals for battery compartments. These technologies can provide a high level of water resistance without compromising the ability to replace the battery. Furthermore, integrating wireless charging technology eliminates the need for physical charging ports, simplifying sealing.
Implications for Manufacturers and Consumers
The EU’s user-replaceable batteries rule will undoubtedly affect manufacturers and consumers. Manufacturers must rethink their design and engineering processes to ensure compliance with the law while maintaining desirable IP ratings. This may require investments in research and development to explore new sealing methods and materials.
For consumers, the rule brings positive changes. It grants them greater control over their devices and promotes sustainability by reducing electronic waste. Users will have the freedom to replace batteries when necessary, prolonging the lifespan of their devices and potentially reducing the overall cost of ownership.
FAQs
Can smartphones with user-replaceable batteries achieve high IP ratings?
While combining user-replaceable batteries with high IP ratings is technically feasible, it poses design challenges. Manufacturers are exploring innovative sealing techniques and materials to address this issue.
Will the EU rule on user-replaceable batteries affect the waterproofing of existing smartphones?
The EU rule primarily applies to new devices manufactured for the European market. The rule may not directly affect existing smartphones, but manufacturers may implement similar designs globally.
What are the benefits of user-replaceable batteries for consumers?
User-replaceable batteries allow consumers to easily replace worn-out or damaged batteries, extending their lifespan and potentially reducing ownership costs.
How will the EU rule impact the smartphone market?
The EU rule will likely lead to smartphone design and manufacturing process changes. Manufacturers must invest in research and development to meet the requirements, which may impact pricing and product availability.
When will the EU rule on user-replaceable batteries go into effect?
The law is expected to go into effect in early 2027, subject to formal endorsement by the European Council. However, the EU may delay the implementation of manufacturers require more time to comply.
Wrap Up
The EU user-replaceable batteries rule represents a significant step toward promoting sustainability and empowering consumers. While there are challenges in achieving battery replaceability and water resistance, ongoing technological advancements offer potential solutions. Manufacturers must adapt their design strategies to comply with the rule while maintaining high IP ratings. Integrating user-replaceable batteries and robust water resistance in mobile devices will ultimately enhance the overall user experience and contribute to a more sustainable future.

Selva Ganesh is the Chief Editor of this Blog. He is a Computer Science Engineer, An experienced Android Developer, Professional Blogger with 8+ years in the field. He completed courses about Google News Initiative. He runs Android Infotech which offers Problem Solving Articles around the globe.



Leave a Reply