In today’s era of portable devices, the endurance of battery life is a paramount concern for users. Despite the impressive battery capabilities of contemporary laptops, unlocking the full potential requires a nuanced understanding of the power management features within Windows 11. This article aims to be your guiding companion, providing a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to activating hibernate mode. By delving into the intricacies of power management, users can optimize their device’s power usage, ensuring prolonged battery life and safeguarding valuable work. From navigating through the Control Panel to exploring advanced settings in the Registry Editor, this guide empowers users to make informed decisions, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency and longevity of their Windows 11 experience.
Understanding Sleep Mode vs. Hibernate Mode
Sleep Mode:
Sleep mode is akin to a power nap for your computer. It preserves the current system state, including open documents and running apps, by saving them to RAM. This low-power state is ideal for short breaks, allowing you to resume your activities swiftly. However, remember that sleep mode still consumes a small amount of battery, and a complete battery drain may result in the loss of unsaved work.
Hibernate Mode:
In contrast, hibernate mode takes a more conservative approach. It saves your system state to a hard drive or SSD, shutting down your system entirely. Unlike sleep mode, hibernate mode consumes zero power, ensuring your battery remains untouched. When you power your PC again, your apps and documents will be where you left them.
Activating Hibernate Mode in Windows 11
Via Control Panel
- Open the Start menu and look for the Control Panel.
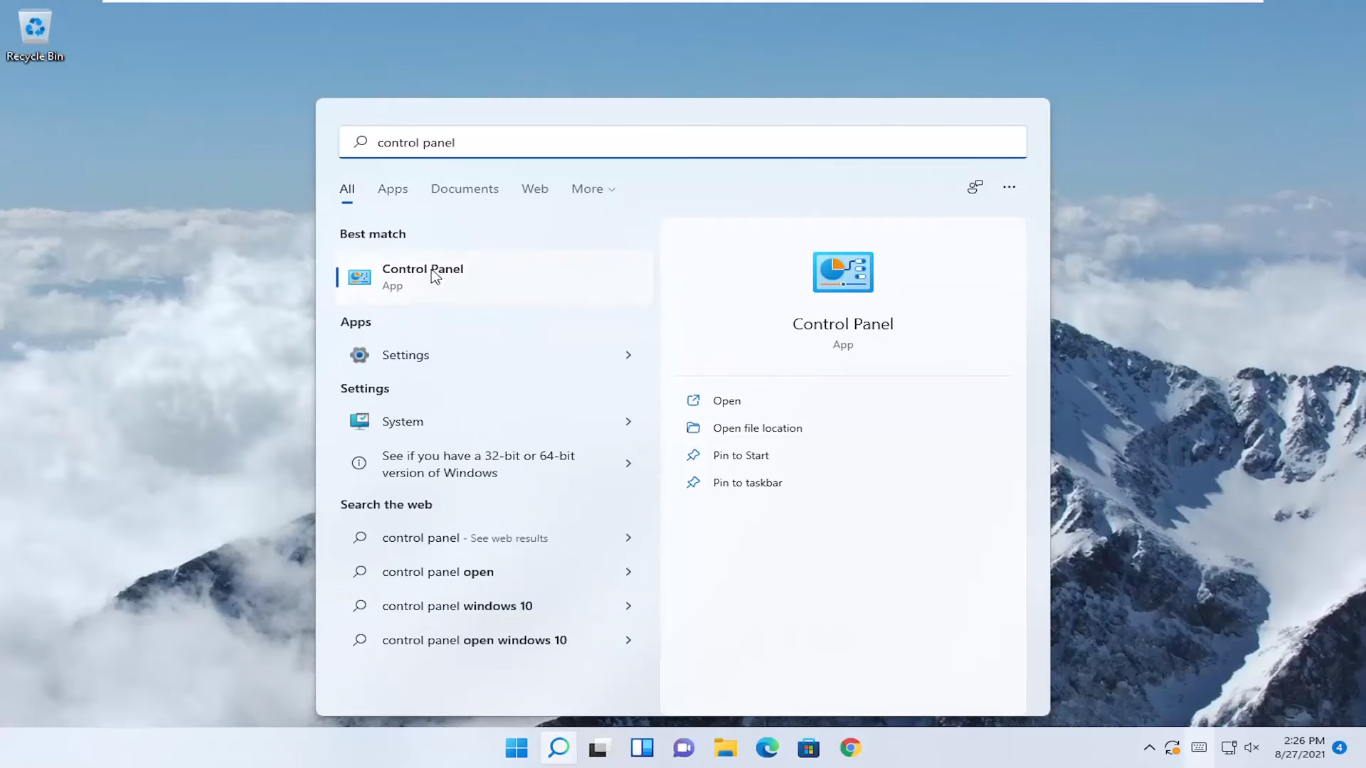
- Click Hardware and Sound in the Control Panel menu.
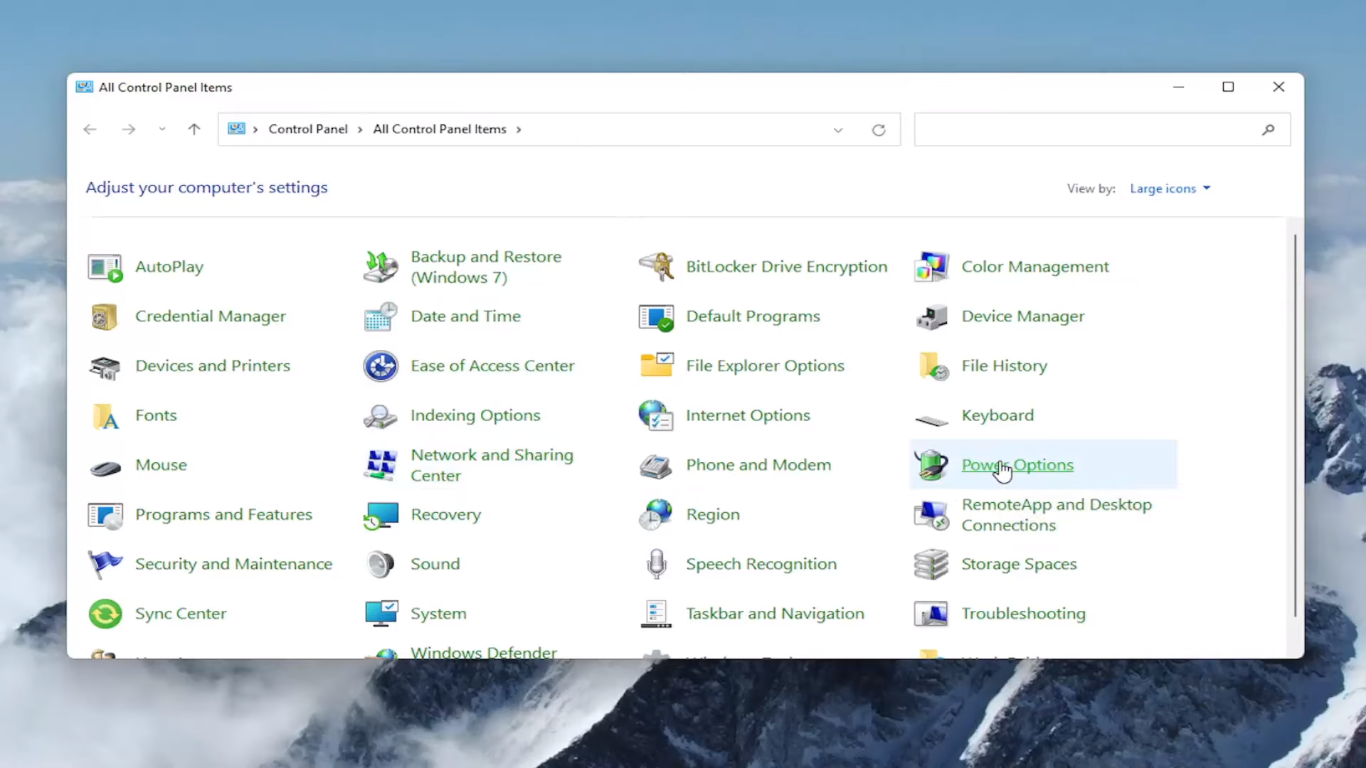
- Under Power Options, select Change what the power buttons do.
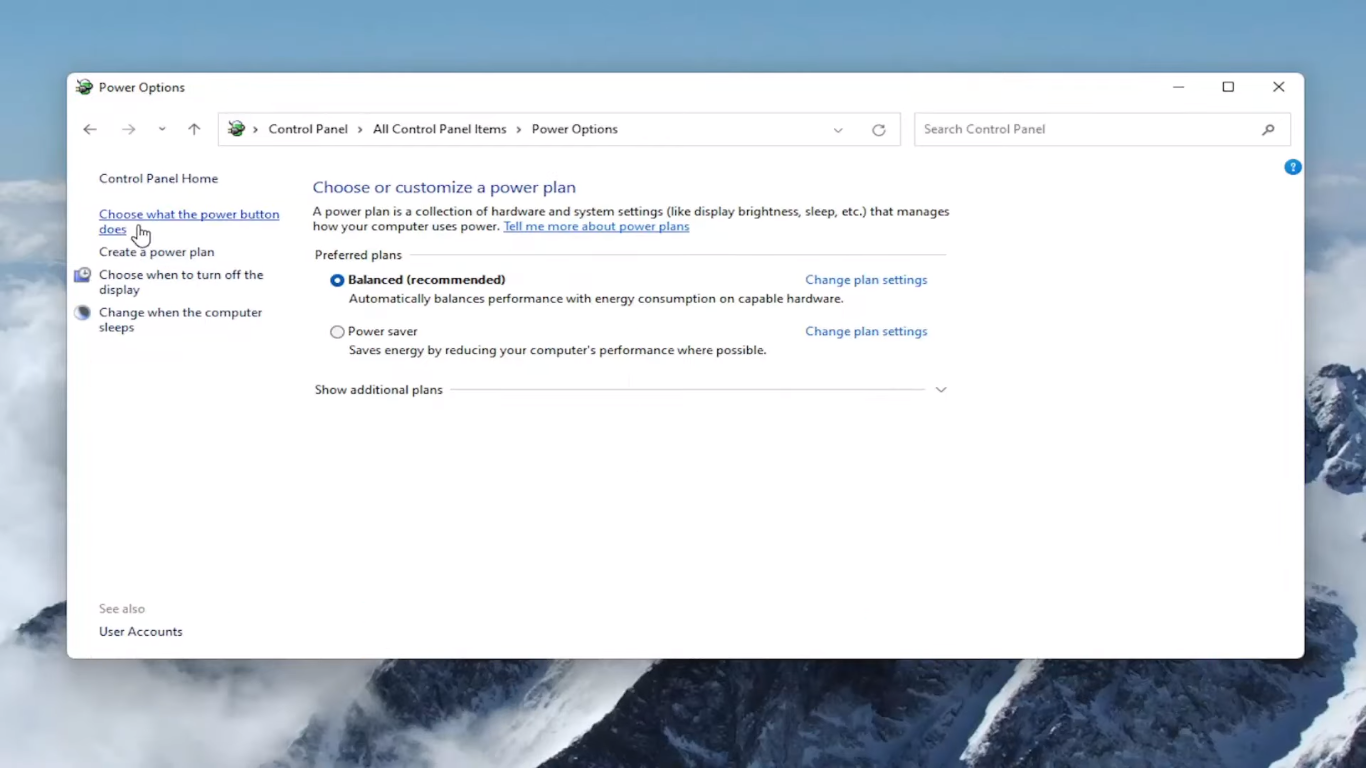
- The Hibernate option may be grayed out; click Change settings currently unavailable.
- Tick the box next to the Hibernate setting and click Save Changes.
Using Command Prompt
If the Hibernate option is missing, follow these steps:
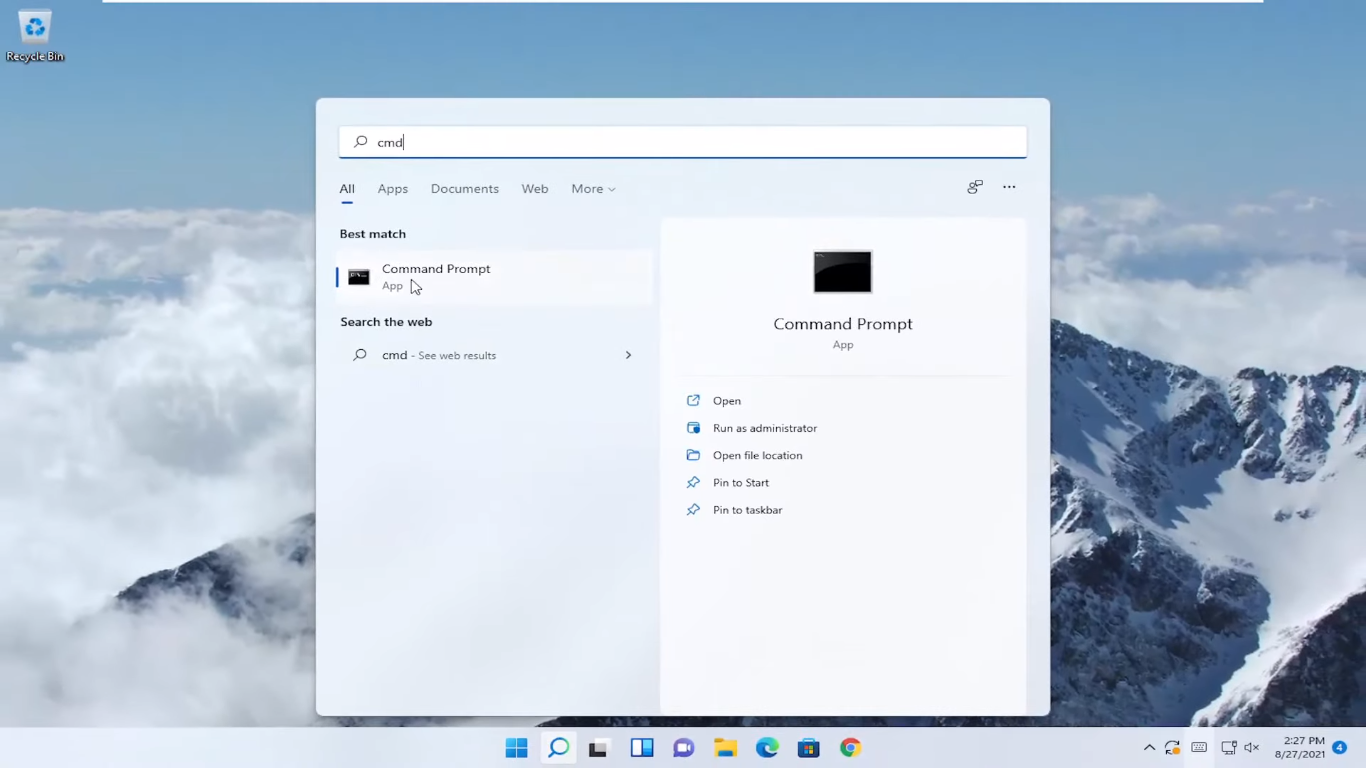
- Look for the Command Prompt application in the Start menu and run it with administrator privileges.
- Type powercfg /hibernate on and press Enter to enable hibernation mode.
- Set the type of hibernation with powercfg /h /type full.
- Find the Hibernate option in the Start Menu’s power menu.
Registry Editor Method
For advanced users:
- In the Start Menu, type Regedit and select Run as administrator.
- Navigate to Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power in the Registry Editor.
- Look for the HibernateEableDefault option in the settings list.
- Double-click on it, adjust the Value Data field to 1 and click OK.
Troubleshooting: Missing Hibernate Option
The hibernation file may be missing if the Hibernate option is not visible. Use the Command Prompt as an administrator to rectify this:
- Look for the Command Prompt application in the Start menu and run it as an administrator.
- Enter powercfg /hibernate to enable hibernation.
- Set the type with powercfg /h /type full.
- Access the Hibernate option in the power menu.
Advanced Method: Registry Settings
For those comfortable with the registry editor:
- In the Windows 11 Start Menu, enter “Regedit” into the search bar and choose to run it as an administrator.
- Navigate to Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power.
- Find the HibernateEableDefault option and set the Value Data field to 1.
Activate Hibernate Mode on Windows 11 to ensure optimal power management and prolonged battery life. Whether through the Control Panel, Command Prompt, or Registry Editor, the choice is yours.
FAQs
What is the main difference between sleep mode and hibernate mode?
Sleep mode saves the system state to RAM, consuming minimal power, while hibernate mode saves it to a hard drive, consuming zero power.
Why is the Hibernate option grayed out in the Control Panel?
The hibernation file may be missing; use Command Prompt to enable hibernation.
Can I activate hibernate mode if I’m unfamiliar with the registry editor?
Use the Control Panel or Command Prompt methods for a more straightforward approach.
Will enabling hibernate mode affect my computer’s performance?
The hibernate mode is designed to preserve the system state without compromising performance.
Is it possible to revert to sleep mode after enabling hibernate mode?
You can choose between sleep and hibernate mode based on your needs.
Wrap Up
Understanding and activating hibernate mode on Windows 11 present a simple yet impactful solution to prolong your device’s battery life. This feature becomes particularly relevant for users who prioritize extended work periods away from a power source. By opting for a method that aligns with your comfort level, whether through the Control Panel, Command Prompt, or Registry Editor, you empower yourself to integrate hibernate mode into your computing routine seamlessly. This choice ensures uninterrupted productivity by preserving your system state and allowing you to pick up where you left off without worrying about battery drain.
Whether navigating through the Control Panel or delving into the more advanced Registry Editor, the flexibility of options caters to users of varying technical expertise, making the activation of hibernate mode a user-friendly enhancement for every Windows 11 user.

Selva Ganesh is the Chief Editor of this Blog. He is a Computer Science Engineer, An experienced Android Developer, Professional Blogger with 8+ years in the field. He completed courses about Google News Initiative. He runs Android Infotech which offers Problem Solving Articles around the globe.



Leave a Reply